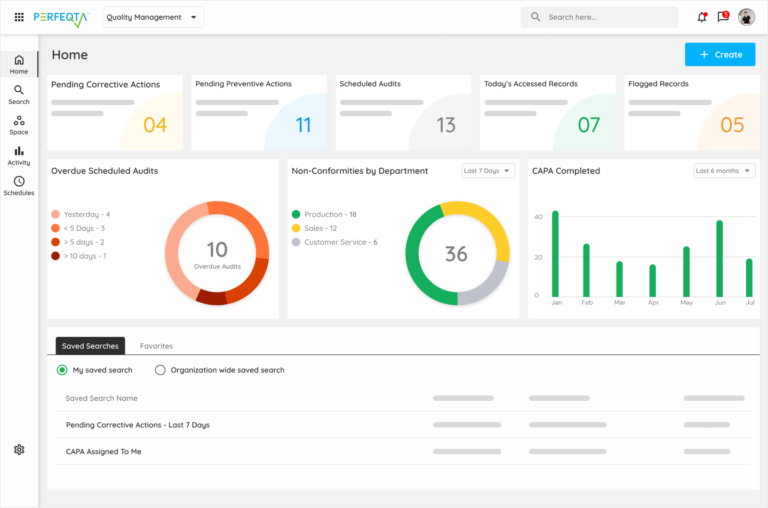
Laboratory Quality Management System

The laboratory quality management system is an essential component of the modern laboratory.
This system is designed to ensure that laboratories produce accurate and reliable results consistently.
The system provides a framework for managing all aspects of laboratory operations, from personnel management to equipment maintenance.
In this blog, we will dive into the key components of the Laboratory Quality Management System.
We will discuss the role of ISO standards in lab management and how they are relevant to ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 17025:2017.
We will also cover the essential components of a Laboratory Quality Management System, including organization and personnel, equipment and inventory management, process control and information management, documents, records, and occurrence management, and assessment, process improvement, and customer service.
Lastly, we’ll touch upon ensuring facility safety in Laboratory Quality Management and how Quality Management Software can enhance Laboratory Operations.
Understanding the Laboratory Quality Management System
Implementing a laboratory QMS, such as the WHO Laboratory QMS Handbook, ensures compliance with ISO standards, including the participation in external audits.
This comprehensive reference on quality management systems in medical and clinical laboratories covers crucial topics necessary for effective quality management in public health or clinical laboratories.
This framework manages quality control and assurance, improving the accuracy and reliability of test results.
It includes processes for purchasing and inventory management while emphasizing effective document control.
By adhering to these standards and participating in external audits, laboratories can demonstrate their commitment to excellence and ensure the highest level of quality in their operations.
Significance of ISO Standards in Lab Management
ISO standards play a significant role in lab management by providing guidelines for establishing a quality management system.
ISO 9001:2015 focuses on overall quality management principles, while ISO/IEC 17025:2017 specifically addresses the competence of laboratories.
Compliance with ISO standards enhances customer satisfaction and trust, and helps laboratories meet regulatory requirements.
Implementing ISO standards is crucial for maintaining high-quality lab operations.
| Aspect | Description | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Policy | Statement of lab’s commitment to quality | Management |
| Organizational Structure | Hierarchical arrangement of lab roles and responsibilities | Management |
| Document Control | Managing lab documents and ensuring their accuracy | Document Control Team |
| Risk Management | Identifying and managing risks associated with lab operations | Risk Management Team |
| Training & Competency | Ensuring lab staff are trained and competent | Training Coordinator |
| Equipment Management | Calibrating, maintaining, and validating lab equipment | Equipment Manager |
| Sample Management | Proper handling, storage, and disposal of samples | Sample Management Team |
| Method Validation | Validating testing methods for accuracy and precision | Method Validation Team |
| Nonconformance & Corrective Actions | Addressing deviations from quality standards | Quality Assurance Team |
| Auditing | Internal and external audits to ensure compliance | Internal & External Auditors |
| Continuous Improvement | Ongoing efforts to enhance lab processes and efficiency | Process Improvement Team |
| Customer Feedback | Collecting and addressing customer suggestions/complaints | Customer Support Team |
How is the Laboratory Quality Management System relevant to ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 17025:2017?
The Laboratory Quality Management System is closely aligned with ISO 9001:2015, which emphasizes customer satisfaction and continual improvement.
Additionally, it incorporates the technical requirements of ISO/IEC 17025:2017, focusing on competence, impartiality, and consistent laboratory operations.
Both standards require internal audits and management review.
Essential Components of a Laboratory Quality Management System
The successful implementation of a laboratory Quality Management System (QMS) relies on several essential components.
The organization and personnel within the laboratory play a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness of the QMS.
Proper equipment and inventory management are vital for accurate testing, while process control guarantees consistency and reliability in laboratory operations.
Effective information management facilitates data analysis and decision-making, while document control and occurrence management are key components of a robust laboratory QMS.
The Role of Organization and Personnel
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities ensure accountability within the laboratory.
Adequate training and competency assessments are essential for personnel.
Effective communication and teamwork promote a quality culture.
Human resources management plays a vital role in maintaining a skilled workforce.
Regular performance evaluations contribute to ongoing improvement.
With the support of a laboratory quality management system, organizations can optimize their organization and personnel to ensure efficient and effective operations.
Importance of Equipment and Inventory Management
Proper calibration and maintenance of equipment are crucial in ensuring accurate test results.
By preventing stockouts and ensuring the availability of required supplies, inventory management plays a vital role in laboratory operations.
Effective management of equipment and inventory reduces potential risks and errors, contributing to the overall quality of testing.
Implementing preventive maintenance programs prolongs the lifespan of equipment, while regular inspections and audits support regulatory compliance.
Process Control and Information Management
Process control measures, including validation, are crucial for maintaining quality standards and preventing deviations.
Effective data management ensures the integrity and traceability of laboratory results, while statistical analysis helps identify trends and areas for improvement.
Information security safeguards protect sensitive patient information, and integration of laboratory information systems streamlines workflow and reduces errors.
By implementing these processes, a laboratory can ensure efficient performance and accurate results.
Documents, Records, and Occurrence Management
Effective laboratory quality management systems prioritize document control, ensuring accurate procedures and instructions.
Proper recordkeeping facilitates traceability and supports compliance audits, while occurrence management processes address non-conformities and incidents.
Root cause analysis identifies corrective and preventive actions, minimizing the impact of document revisions through effective change control processes.
These measures, endorsed by organizations like the World Health Organization and the CDC, ensure a robust internal audit program and adherence to laboratory standards.
The implementation of quality control (QC) modules and CAPA enhances the overall laboratory quality management system.
Why is Assessment, Process Improvement, and Customer Service vital?
Regular assessments and internal audits ensure ongoing compliance with standards, while continuous process improvement drives efficiency in the lab.
Customer feedback and prompt addressing of concerns enhance trust, loyalty, and overall experience.
Proactive customer service is crucial for a successful laboratory quality management system.
Ensuring Facility Safety in Laboratory Quality Management
Maintaining a safe laboratory environment is crucial in the Laboratory Quality Management System (LQMS) for public health.
By adhering to relevant safety regulations, such as those set by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), risks to personnel and the public are minimized.
Regular inspections and risk assessments play a vital role in identifying potential hazards, while training programs ensure safety awareness and proper handling of hazardous materials.
Additionally, emergency response plans and drills ensure preparedness for any unforeseen incidents.
How does Quality Management Software enhance Laboratory Operations?
Quality Management Software (QMS) plays a vital role in enhancing laboratory operations.
It streamlines processes, improves information management, ensures regulatory compliance, and enhances process control.
By implementing QMS, laboratories can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and overall quality in their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing a Laboratory Quality Management System (LQMS) is crucial for ensuring accuracy, reliability, and compliance in laboratory operations.
It helps laboratories meet ISO standards, such as ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 17025:2017, and maintain consistent quality throughout their processes.
Key components of an effective LQMS include organization and personnel management, equipment and inventory management, process control and information management, document and record management, and continuous assessment and improvement.
Additionally, prioritizing facility safety and utilizing quality management software further enhances laboratory operations.
If you want to streamline your lab’s processes and achieve optimal quality, sign up for our LQMS solution today.